Cold Bridging (also known as Thermal Bridging or Heat Bridging) occurs in a building where there is a gap in the insulation such as a join or corner or where a structural element spans across thermal insulation (for example in timber frame panels). Vision Development use a number of measures to overcome cold bridging in our closed panel timber frames thus improving thermal insulation and energy efficiency.
For our most energy efficient closed panel timber frame, Vision Development applies an additional layer of solid insulation on the outside face of the panels. This overcomes the thermal bridges that are evident if insulation is only applied within the timber studs (inside the timber frame panels).
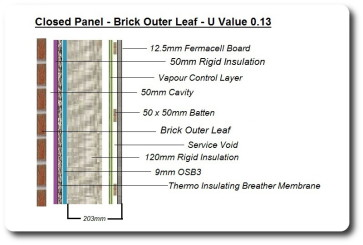
The U values shown in the diagrams on the right are achieved using a 120mm layer of solid petrochemical based insulant between the 140mm studs within the panel. The insulation is fitted within the panels in a factory environment improving quality control and ensuring a precise fit. The panels are also of a reasonable width of approximately 203mm so that they do not encroach in your living spaces. The panels reduce costs for heating, improve air tightness and greatly reduce cold bridging. These diagrams show how the panels are constructed but they can be adapted to suit particular requirements.
In addition, a 50mm layer of solid petrochemical based insulant (coloured purple in the diagrams) is applied to the ‘outside’ of the timber frame in the cavity between the panel and the external cladding or bricks. This will over sail the timber studs, therefore eliminating thermal bridging and achieving a lower U Value. Care needs to be taken to ensure a tight fit against the external face of the racking board so that energy is not lost through air movement (convection).
The images on the right show a 140mm frame filled with 120mm of rigid insulation and 50mm of rigid insulation in the cavity between the frame and the external cladding. With this structure we can achieve a U Value of 0.15 with external timber cladding and 0.13 with external brick.
Installing a service void to the internal side of the timber frame helps to ensure that the insulation, vapour control layer and air tightness membrane are left undisturbed. This helps to prevent any air movement within those layers as convection will significantly reduce the performance of the insulation.
To meet the requirements of the accredited construction details (ACDs) insulation should be taken below the Damp Proof Course (DPC) so that thermal bridging does not occur below the DPC.
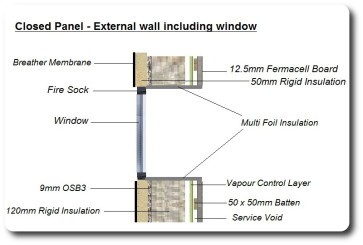
The windows should be installed within the timber frame & insulation layers to help eliminate thermal bridging. However, if windows are fitted to the external face then the window reveals need to have a layer of insulation fitted to further assist in reducing cold bridging. Multi Foil insulation is shown in the diagram on the bottom right. The fire sock around the windows also acts as a thermal insulator. Air sealant tape is applied around the windows for air tightness.
If you want to know more about how you can use our closed panel timber frames to construct energy efficient buildings and extensions please contact us by calling 0118 971 2181 or by email or by using our contact form.